Mean:
The mean is the sum of scores divided by the number of scores.
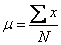 where
where 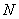 is the number of scores.
is the number of scores.
Mode:
Mode of a set of data is the value in the set that occurs most often.
Range:
The range of a set of data is the difference between the highest and lowest values in the set.
Variance:
The variance of a sample measures how the conservations are spread around the mean.
Standard Deviation:
The standard deviation is the square root of the average of the squared deviations from the mean (variance).
Categorical frequency distributions:
Categorical frequency distributions can be used for data that can be placed in specific categories, such as nominal- or ordinal-level data.
Central Limit Theorem:
As the sample size increases the sampling distribution of the sample mean approaches the normal distribution with mean 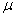 and variance
and variance 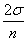 .
.
The exponential, binomial, and normal density functions:
The exponential, binomial and normal density functions are used along with their respective probability distributions to approximate statistical models and values.